Set-Up
Add a sphere. Increase the segments and change the segment type to hexahedron.
Simulation works best with real-life sizes.
Rock
Step 1
Make an instance of the sphere.
Instances are lightweight copies of an object that do not contain any geometry data, but rather maintain a link to the original object.
Add a Voronoi Fracture to the instance. Adjust the sources panel.
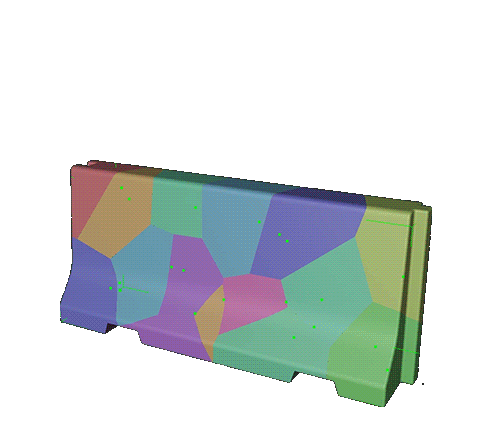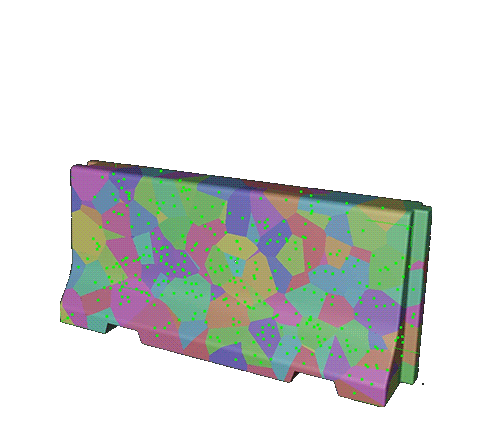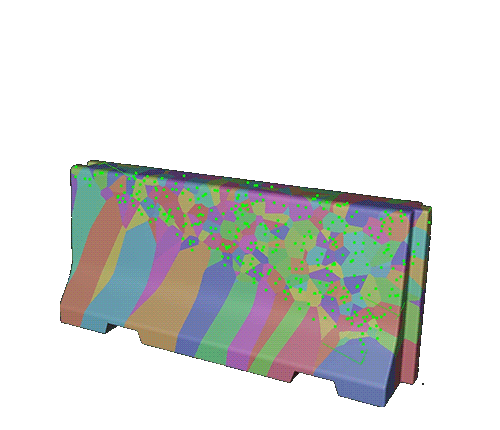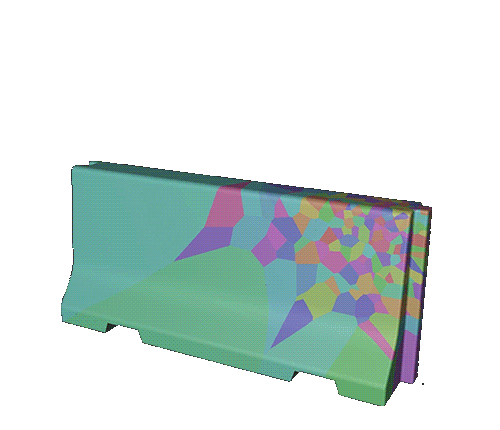
of the voronoi points
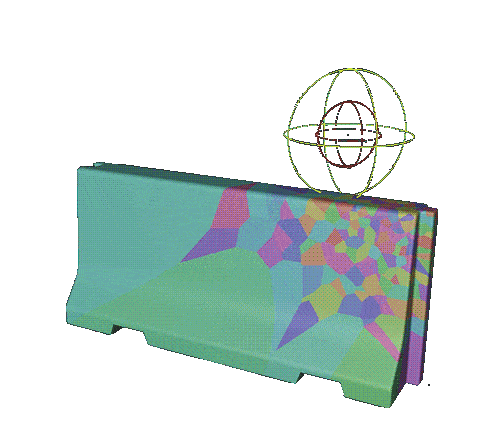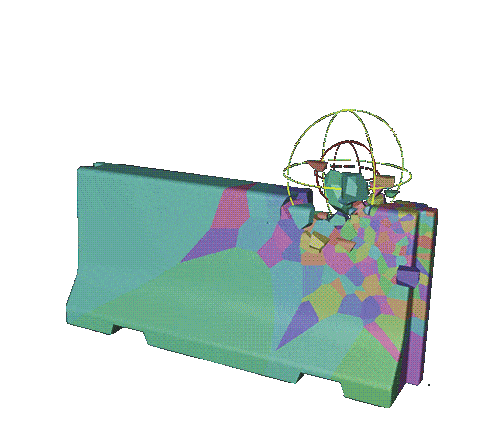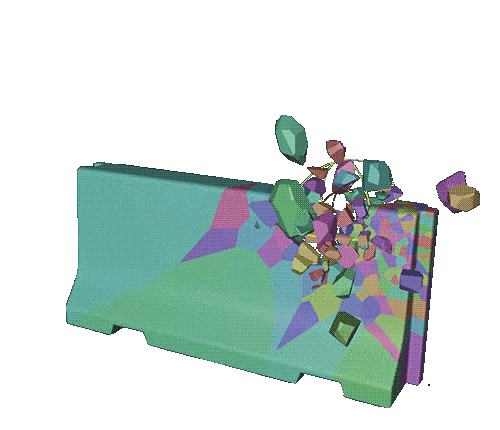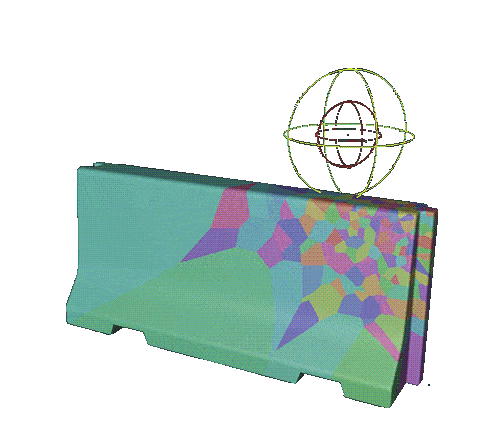
how the effect will be triggered
Step 2 Adding animation
Create a push apart effector and a random effector.
Goo
Step 1 Using Boole
Create another instance of the sphere and one of the voronoi.
Add a Boole effector. Set the scale to 0.95. Switch the type to A without B.
Check the boxes for “create single objects” and uncheck “hide new edges” and “high quality”.
Step 2 Using MoExtrude
Create a MoExtrude to the Boole. Set the P.Z transform to 1.
Add a plane effector to drive the MoExtrude.
After zeroing out the Y scale, set the scale.

Add a smoothing deformer and put it below the MoExtrude. Adjust the stillness and iteration.
Step 3 Using Volume Builder and Volume Mesher
Add a Volume Builder and a Volume Mesher to the MoExtrude. Adjust the voxel size. Check the “use mesh points” and adjust the radius.

Volume Builder and Volume Mesher can be used to create objects that are made of multiple child C4D objects.
Add an SDF Smoothing and an SDF Close and Open on top of the Boole.
There are two types of volume in volume builder: SDF and Fog. (Vector is also an option but is quite different.)
Signed Distance Field (SDF) can be used when a Boolean operation has to be applied when modeling because polygons, points, and particles themselves have no volume. In order to generate volume, layers of Voxels are placed around these elements (over and under polygon surfaces).
Add a random field in the plane effector panel. Adjust the scale and types of noises.


Render Set-Up
Lights and Background
#redshift